SnapLogic
Last Updated:
Analyst Coverage: Philip Howard and Daniel Howard
SnapLogic was founded in 2006 by Gaurav Dillon one of the co-founders and ex-CEO of Informatica, and the product was officially launched in 2013. It is backed by venture capital, having raised in excess of $200m to date. The company’s headquarters are in California and it also has offices across Europe, Australia, India and the UK.
SnapLogic is focused on enterprise-level (Global 2000) solutions and has more than 2,500 subscribers – subscription is the only licensing option – spread across all industry verticals. The company has a widespread partner network of all types. Notable technology partnerships include all the leading cloud providers, HVR Software (to provide change data capture, something not present in the SnapLogic platform), AWS, Cloudera, SAP, Tableau, Snowflake, Splunk, Microsoft, Salesforce and Workday, amongst others.
SnapLogic in the Data Fabric
Last Updated: 2nd April 2024
Mutable Award: Gold 2024
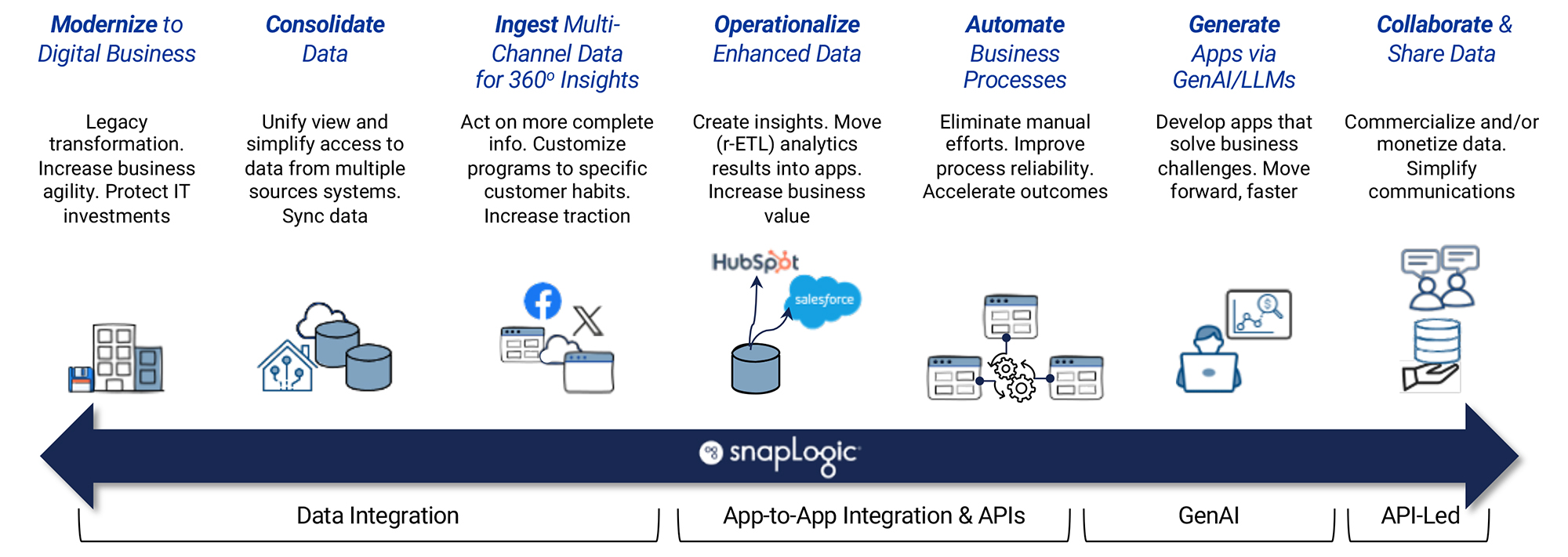
SnapLogic’s core capability is codeless app and data integration. It has a visual designer to help design and build data pipelines with over 1,000 pre-built connectors (“Snaps”) and patterns, connecting to and from popular data sources like SAP, Salesforce, ServiceNow, Netsuite, leading databases, and more. A cloud-native application itself, SnapLogic allows integration of data between cloud and on-premises systems, supporting both batch and near real-time streaming. It also orchestrates and automates business processes and workflows. Its visual designer interface is intended to allow end users to build their own data pipelines with minimal assistance from the IT department. While at the same time, providing IT a flexible, visually driven integration productivity enhancer that also can be customised and driven deeper, under the hood, when necessary.
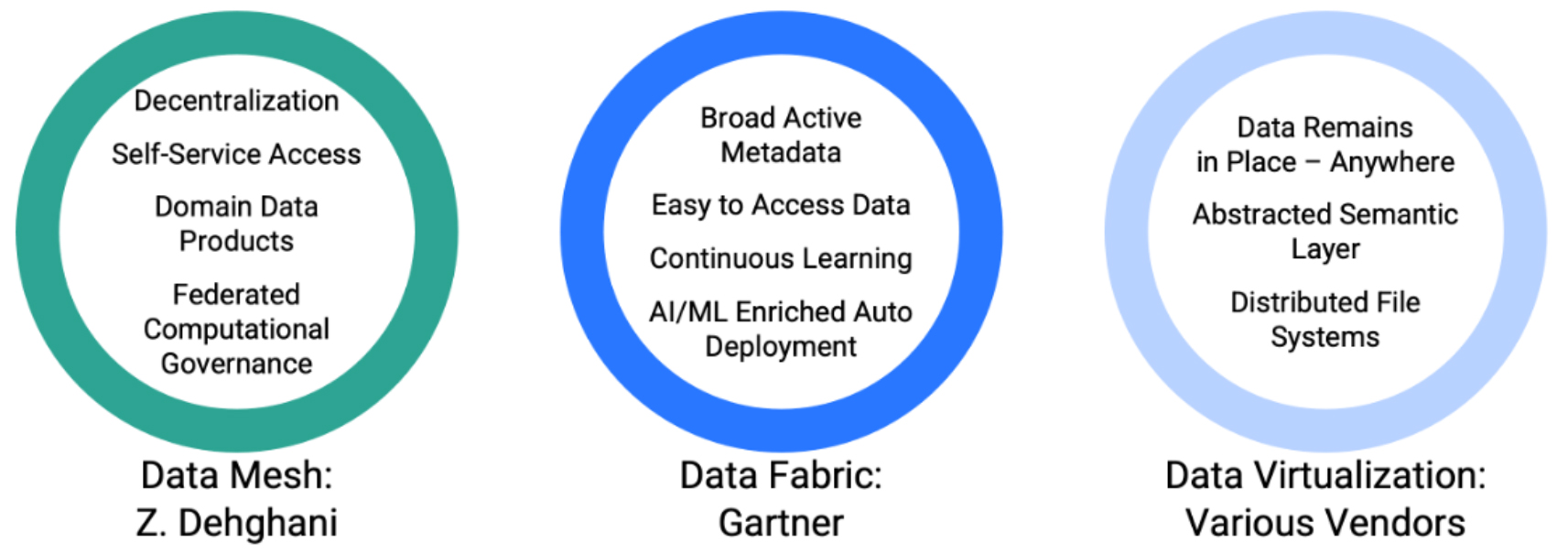
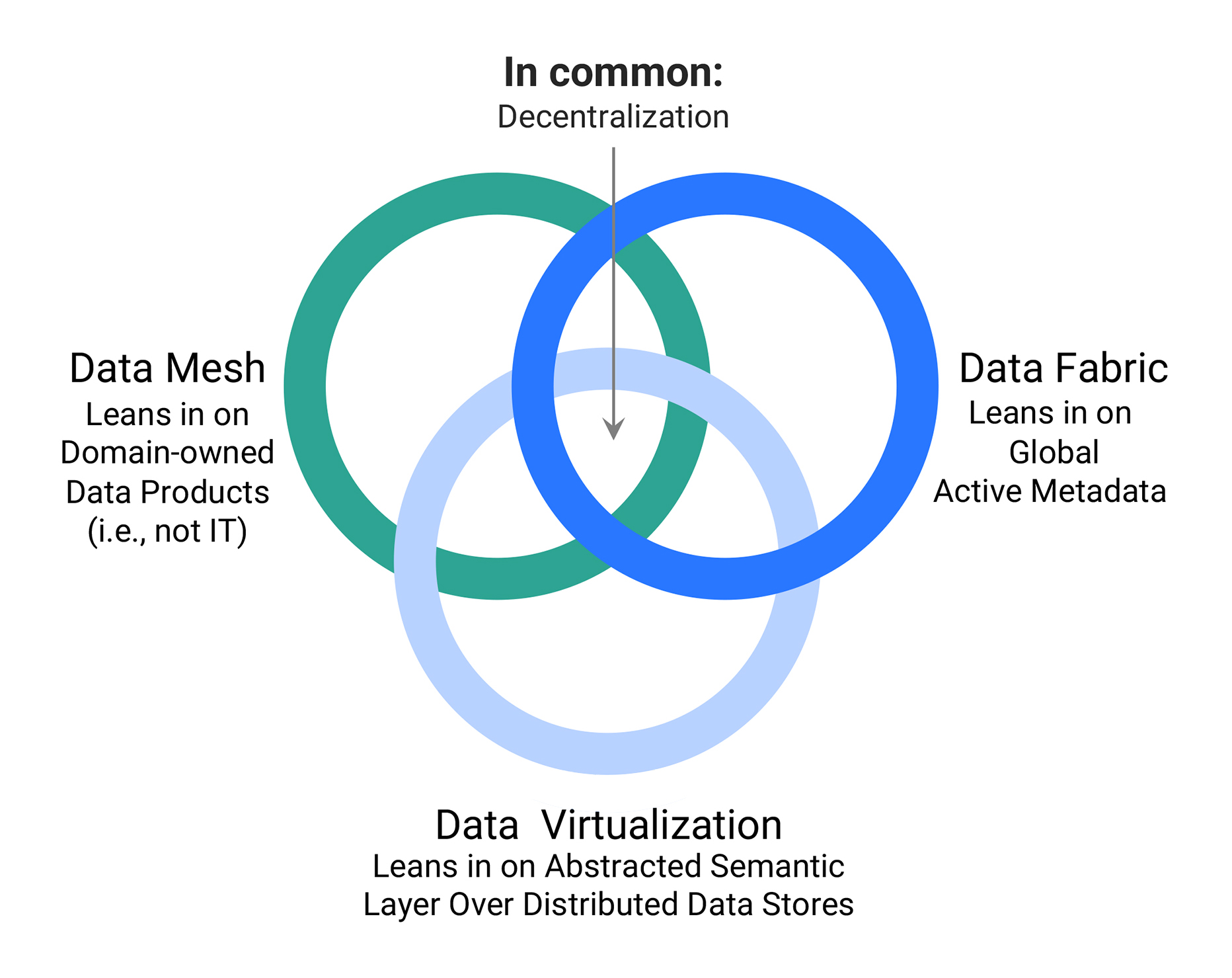
In terms of data fabric and data mesh architectures, Snaplogic sees these architecture approaches as overlapping, offering different strengths, but sharing in common a principle for decentralisation. SnapLogic supports these approaches in several ways. With an emphasis on self-service data pipeline and data product creation and management. SnapLogic provides an AI-augmented integration infrastructure that is multi-domain capable, and can be federated. This includes cataloguing and version control of API-driven data products. SnapLogic can ingest, transform and serve up data packages from widely distributed source systems, but federate control and security. The solution has inherent support for project-based data products by business domain, so fitting neatly within the data mesh concept of distributed data ownership, but with federated control and security, simplifying deployment. It can publish API-Led data products through an internal data marketplace or portal. It is not a complete data fabric solution, but then arguably no one vendor provides everything for a data fabric at present. It is certainly the case that no one vendor currently provides a complete data mesh solution.
Customer Quotes
“It takes us minutes to deploy integrations across 1,800 applications with SnapLogic. We have also been able to reduce overhead and support costs by 25%.”
Swati Oza, Director of IT Emerging Technology, Data Integration and Machine Learning at Hewlett Packard Enterprise
“SnapLogic is our secret weapon. We are able to deliver on the company’s digital transformation initiatve by demonstrating that we can deliver and scale without massive product teams.”
Phil Maguire, Application Service Delivery Manager, ITV
Apart from the core integration functionality described, SnapLogic also has substantial capabilities in artificial intelligence. One example of this is that, for some time, it has been shipping AI-driven AutoSuggest (formerly Iris AI), which dramatically simplifies and speeds up integration builds. Another example is with its SnapGPT copilot, a natural language prompt allowing users to build pipelines, generate sample data or analyse and document existing data pipelines. Lastly, SnapLogic’s GenAI Builder tool was released in January 2024 and allows customers to create their own knowledge store in a vector database (currently Pinecone, with OpenSearch as an option soon) and perform retrieval augmented generation (RAG) by easily loading users structured & unstructured data into a vector database. For example, an employee HR handbook may be indexed and then a natural language interface can be used to answer employee questions like “When will I get paid?”. The private vector database avoids the well-known security issues of public AI tools. There is prompt engineering to ensure that answers are only given within the allowed context, so you get far fewer hallucinations than with general-purpose AI tools like ChatGPT. The product supports OpenAI, Azure Open AI, Claude and Titan (on AWS). One early customer is a utility in waste management that has complex billing formulas in its commercial contracts. They are using the AI capability to accurately extract payment formulas from the contracts for comparison with their billing system, highlighting billing discrepancies. SnapLogic enabled this company to find a significant revenue recovery opportunity and SnapLogic’s ease of use allowed the client to complete a proof of concept in less than 3 days.
The SnapLogic approach allows the creation of custom data integrations to be either accelerated through IT or delegated to and owned by business domain end-users rather than languishing in a work queue within the IT department. In one customer example, Schneider Electric (a $36 billion revenue, French multinational company specialising in digital automation and energy management) – has over a thousand users provisioned on Snaplogic. They have several categories of end users, from advanced ones who need no IT support, to less experienced user categories, and chargeback more to the least experienced users. This gives a direct incentive for users to become more self-reliant and use the tool themselves. Over 30%, and growing, of Schneider Electric integrations have been constructed by citizen integrators.
The bottom line
SnapLogic has made rapid commercial progress in the data and app-to-app integration market, and has many examples of customers where end users, with some degree of technical savvy, really are building their own data pipelines and API-led data products. This is particularly suited to the data mesh idea of distributed data ownership, and can also be applied to more centralised data fabric architectures. SnapLogic should be carefully considered as one of the main building blocks of a data fabric or mesh solution.
SnapLogic Intelligent Integration Platform
Last Updated: 4th February 2021
Mutable Award: Platinum 2020
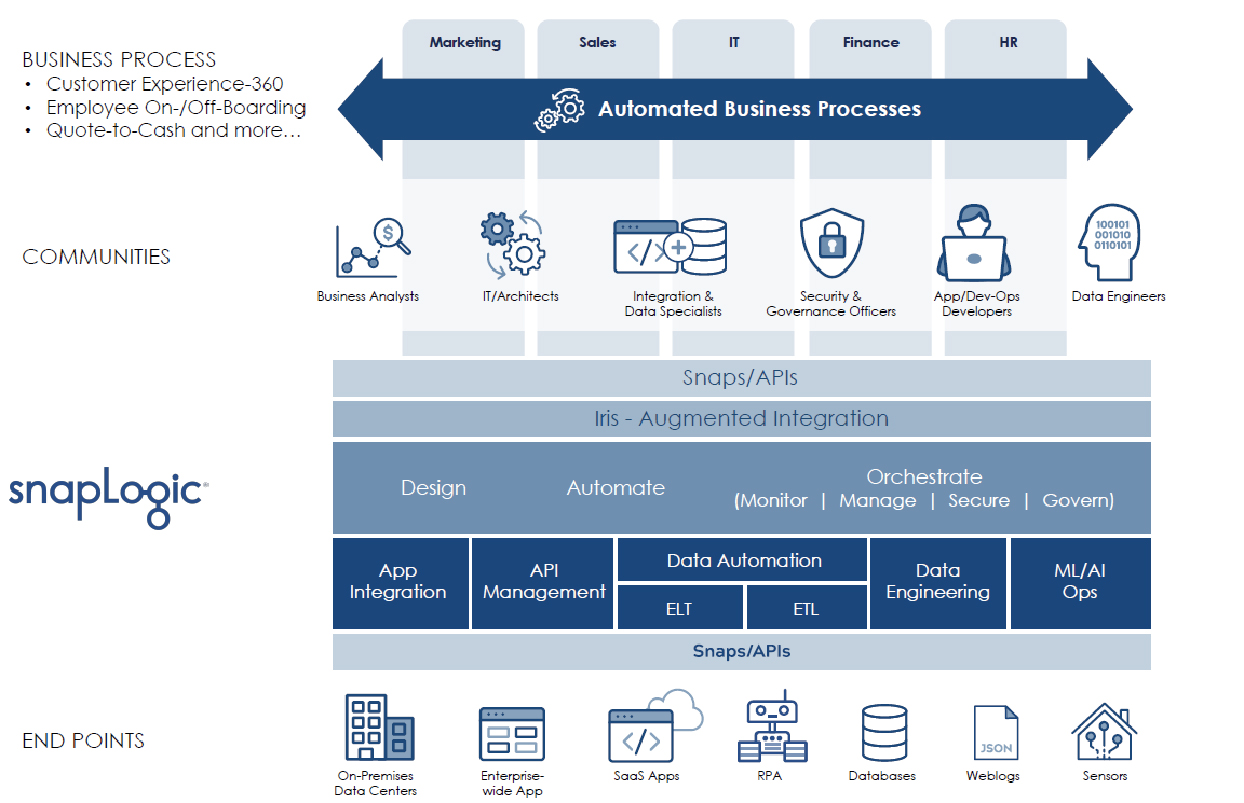
SnapLogic was founded as a provider of application and data integration solutions, but its Intelligent Integration Platform is much broader than that, as Figure 1 illustrates, though we would argue that application integration and even API integration are still actually about moving data. However, SnapLogic Data Science is certainly an extension to data integration, offering both data preparation and model training and development, with the Intelligent Integration Platform taking care of model deployment. As with other elements of the platform this provides a self-service, no/low-code approach to development.
Customer Quotes
“With insights derived through SnapLogic, we are empowered to prepare the next generation of learners and help define their careers.”
Tapan Parekh, Director of Engineering and Architecture, Kaplan Test Prep
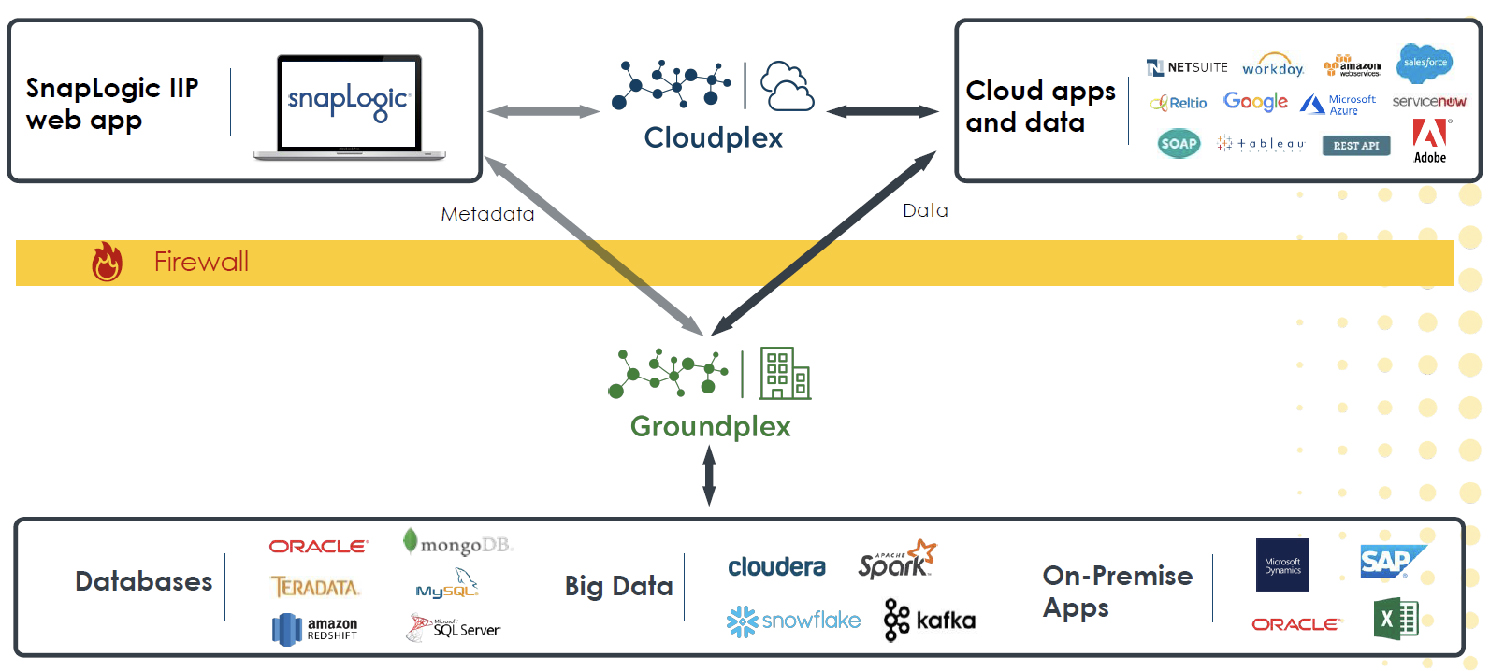
The key elements of SnapLogic are Snaps and Snaplexes. Snaps are connectors, of which the company provides more than 500 out of the box, and which may be directed towards either structured or unstructured data, including B2B interchange formats such as HL7 or EDIFACT. There is also an SDK for developing your own snaps, you can leverage SOAP or REST, and you can even write scripts using Java, Python or JRuby in the Script Snap, or develop your own Snaps using the provided Java SDK. As far as Snaplex is concerned this is the data processing engine, of which there are two versions: Cloudplex, which runs in the cloud; and Groundplex, which is available in the customer domain, on-premises, or in your choice of cloud. These are shown in Figure 2. Note that data is never within the SnapLogic environment per se, only metadata. The Control Plane serves as the web browser-based user interface, as well as storing the metadata, providing authentication, authorisation, scheduling and relevant management functions to the platform as a whole.
SnapLogic refers to its solution as a “streaming data platform” and, while it supports streaming software such as Kafka, this is not what the company means. It is in fact referring to the fact that one step in a data pipeline will not have to complete before the next step begins. This is important for performance reasons. While on the subject of pipelines there are several other comments to make. To begin with, pipelines can call other pipelines. In addition, the Iris AI engine built into the Intelligent Integration Platform can make suggestions with respect to pipelines (and Snaps) that you might want to use. The software also has the ability to check the validity of any pipeline you define, and it can show you a preview of the results.
Going back to Iris we should say that SnapLogic was an early adopter of machine learning (and natural language processing) and it is significantly ahead of many of its competitors in exploiting this, adding productivity to the SnapLogic development environment. Iris is powered by the SnapLogic Data Science capability.
Finally, there is a Fast Data Loader, providing both schema and data replication, offered within the context of the platform. Unfortunately, it is currently relatively limited in terms of the sources (Oracle, SQL Server, Salesforce, Coupa and Servicenow) and targets (Snowflake, Amazon Redshift and SAP DW Cloud) it supports at present, though the company will be building these out over time. As an alternative or in addition, there is SnapLogic eXtreme which is a managed service for big data environments, which supports the population of NoSQL-based data lakes and lakehouses. It is based on a serverless environment and supports elastic scaling.
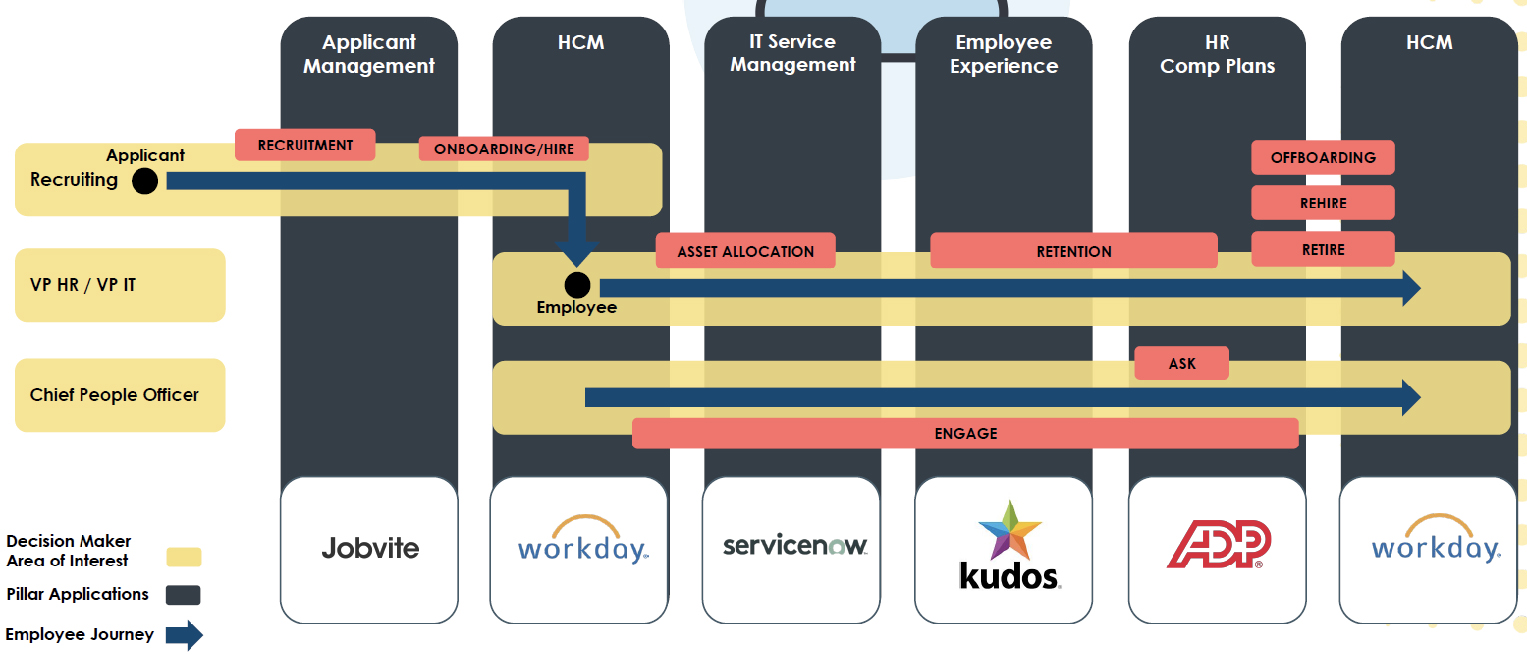
As an integration platform SnapLogic is enterprise-ready (with load balancing, failover, security, resilience and so forth), supports a range of personas and is significantly ahead of many of its rivals when it comes to automation. It has an extensive array of Snaps including those that support sensors and other edge devices within Internet of Things environments. However, perhaps its most important feature is its breadth and the corporate vision that underpins that breadth. The company sees its role as providing what it calls “application automation”. That is, the end-to-end provisioning of pre-built business processes. An example of this is illustrated in Figure 3. In this context, the company is focusing on the development of accelerators to support these cross-silo journeys, including the provision of relevant pre-built and automated processes.
One thing we would like to see is SnapLogic partner with data quality governance and catalogue vendors. No doubt it will work with providers of these technologies but formal partnerships tend to be looked on more favourably than mere integrations.
The Bottom Line
The SnapLogic Intelligent Integration Platform is comprehensive. And, as a pure-play (ignoring SnapLogic Data Science) integration vendor it has a breadth that few if any other vendors can match. We especially like its vision of application automation and its use of machine learning.
Commentary
Coming soon.